Imagine zooming in millions of times into your body until you reach the innermost part of your cells. A group of scientists at UiO is doing just that, to help researchers all over the world prove their theories.
News - Page 14
Half of the veterinarians with serious suicidal thoughts reported that their job was the most important contributing factor.
Artificial intelligence and the cell's self-cleansing system are the keys behind the novel medication. The treatment may strengthen other organs as well.
Helsam researchers are part of a new Helsinki-led network that recently received workshop funding from The Joint Committee for Nordic research councils in the humanities and social sciences (NOS-HS).
We can prevent and treat liver diseases. New treatments are entering clinical practice. However, the treatment does not always reach the patients.
Was it that you should be careful when taking two medicines at the same time, and should you be lifting heavy things? Health professionals should employ a definite strategy when giving patients information, researchers maintain.
Some do well after cardiac arrest, while others get serious injuries and lose their lives. The innate immune system turns out to be part of the explanation.
Public health mitigation measures such as social distancing, closing training centers and wearing face masks have been used during the Covid-19 pandemic. However, the benefits and harms of these measures are poorly understood.
A Mediterranean diet can provide many health benefits, but you may risk consuming too many environmental contaminants. Organically produced food can be the solution, a new study shows.
Unfinished DNA repair contributes to the damage and age-related loss of neurons. However, it might be possible to protect the nerve cells, which may have implications for the prevention of Parkinson’s disease.
Impaired heart function does not seem to be the reason why it takes a long time for some to recover after undergoing COVID-19.
Are you a researcher with an innovative idea based on your research that can contribute to solving an important need in society, but need funding to develop the idea further? Check the UiO call for innovation funding within all academic fields. The call is aimed at both commercial and non-commercial projects. Application deadline: 1 September 2025.
Using MRI images, the researchers were able to see that patients who developed cognitive impairment, had changes in the brain that had occurred before the stroke.
And women with this diagnosis miss out on active treatment time because of pregnancy.
Influenza is a well-known trigger for heart disease. Strict measures to prevent the spread of the coronavirus may have contributed to less influenza, and thus fewer admissions for heart disease.
It is not necessary to tailor the medication doses to patients, at thestart of treatment, for patients to have a good effect. This is shown by a new Norwegian study led by Professor Espen A. Haavardsholm.
Liver encephalopathy is one of the diseases that claims most lives worldwide. A Norwegian study has revealed that the disease disturbs vital processes in the brain.
Protein in the blood did not have the function researchers believed in the interaction between two of the body's defence systems. Professor Tom Eirik Mollnes and colleagues thereby changed an established truth.
The findings may be important for future prevention and treatment, and are an important step towards more knowledge about the causes of bipolar disorder.
The technology, consisting of a designed variant of a natural occurring protein called super albumin, can pave the way for the development of long-acting drugs. This can have major implications for individuals suffering from haemophilia.
According to a survey following doctors over 20 years, nearly four out of ten doctors have been the target of threats from a patient during the first four years after graduation and one in seven doctors have been physically assaulted.
It is safe to be physically active outdoors without having to worry about the risk of melanoma, as long as you follow the sun safety advice, say the researchers behind a large, Norwegian study.
Health care personnel who contributed to the rescue work after the 22 July 2011 terror attacks had better mental health a year later than individuals who contributed as volunteers.
One out of ten E. coli samples contained variants that are resistant to several kinds of antibiotics. Researchers warn that we must monitor the future development of antibiotic resistance carefully.
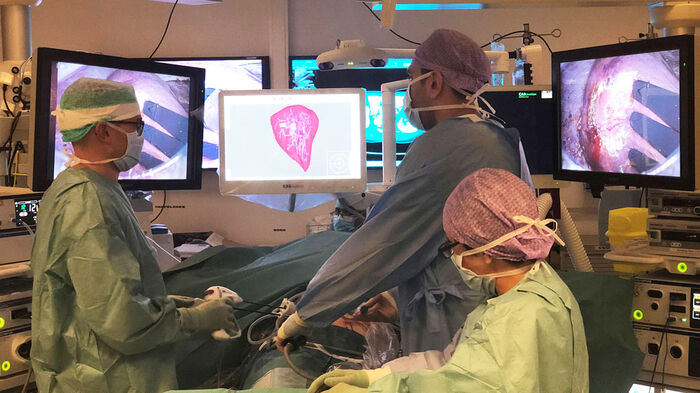
Those who had tumours removed from their livers with keyhole surgery had fewer complications, a better quality of life and similar long-term oncologic outcomes, a new PhD thesis shows.